Weight loss is a complex journey often simplified to just diet and exercise. However, the impact of hormones on this process is profound yet frequently overlooked. This article delves into the intricate role hormones play in weight management. From the metabolism-regulating thyroid hormones to insulin’s critical function in glucose regulation and the stress hormone cortisol, each plays a unique role in our weight loss journey. By understanding these hormonal influences, we can adopt a more holistic and effective approach to achieving and maintaining a healthy weight.
Understanding Hormones and Weight Loss
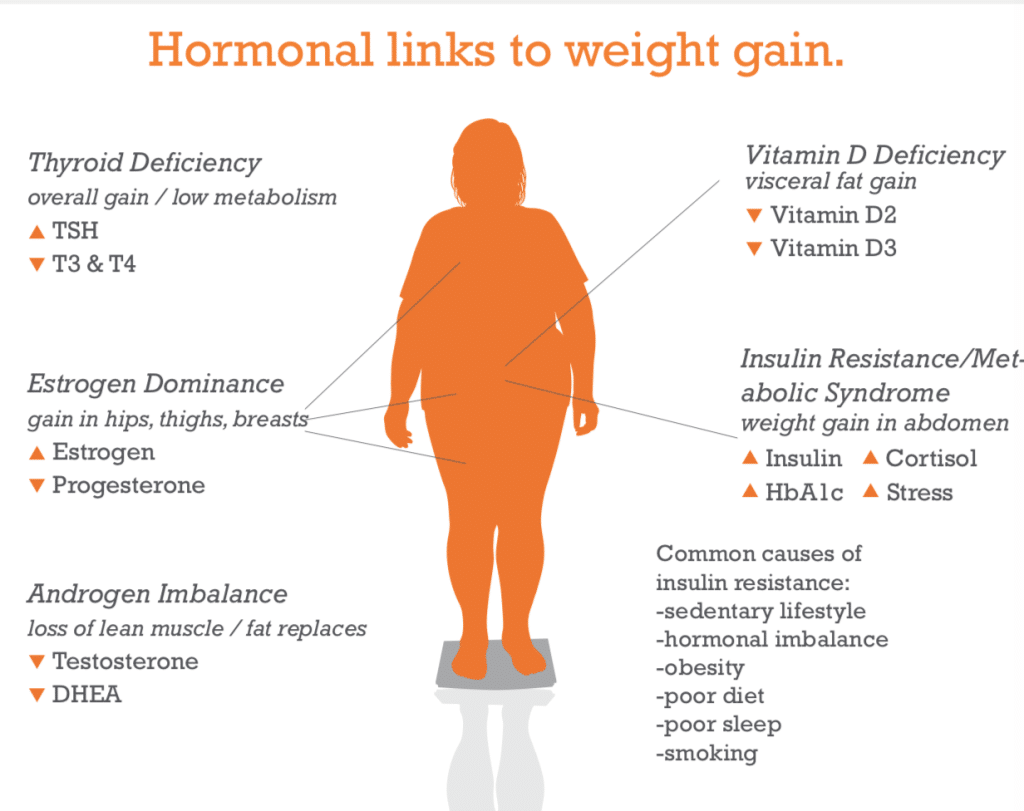
Hormones are biochemical messengers that profoundly influence numerous bodily functions, including weight management. They operate as a complex network, sending signals that regulate appetite, metabolism, and fat storage. This section explores the integral role of hormones in weight management, emphasizing their influence beyond mere calorie counting and physical activity. Understanding this hormonal interplay is crucial for anyone embarking on a weight loss journey, as it can provide insights into why some traditional methods may fail and how to tailor a more effective approach.
Key hormones like thyroid hormones, insulin, cortisol, leptin, and ghrelin will be the focus of this discussion. Each hormone has a specific role, and an imbalance in any of these can significantly derail weight loss efforts. This understanding not only empowers individuals with knowledge but also highlights the importance of a well-rounded approach to weight loss that goes beyond diet and exercise, encompassing a broader view of bodily functions.
Thyroid Hormones and Metabolism
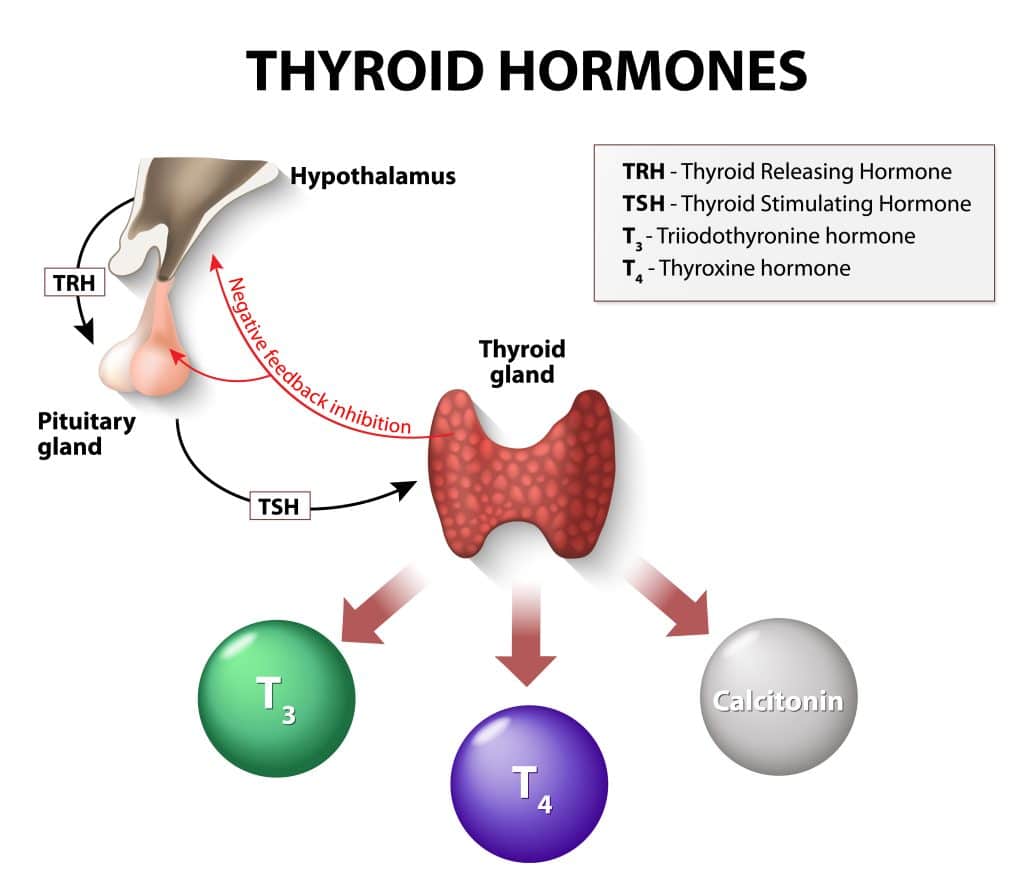
Thyroid hormones, primarily triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4) are critical in regulating metabolism, the body’s energy-using process. They determine the speed of the metabolic processes, influencing how quickly or slowly the body burns calories. An imbalance in these hormones, such as in conditions like hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism, can lead to significant weight challenges. Hypothyroidism, for instance, slows metabolism, often leading to weight gain, whereas hyperthyroidism can have the opposite effect.
This section will delve into how maintaining a healthy thyroid function is key to effective weight management. It’s not just about the quantity of food consumed or the intensity of physical exercise; it’s also about how efficiently the body uses this energy. Practical advice on promoting thyroid health through diet, lifestyle, and potential medical interventions will be provided. This information is vital for anyone struggling with weight management, as it could reveal an underlying thyroid issue as a contributing factor.
Insulin’s Role in Weight Management
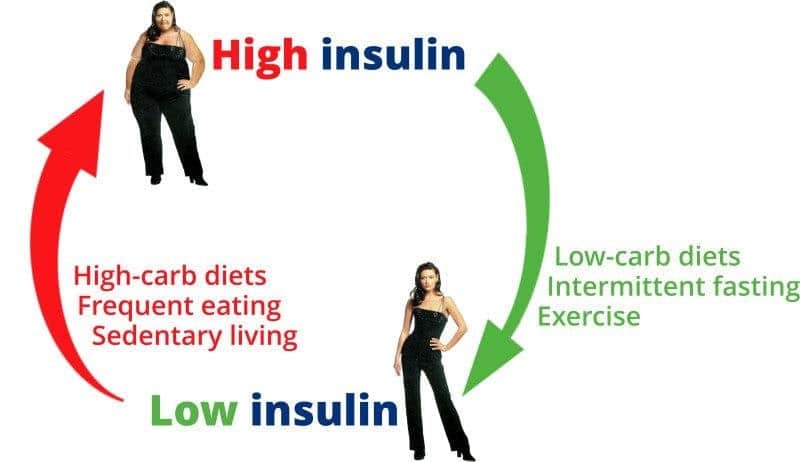
Insulin, a hormone produced by the pancreas, is essential in regulating blood glucose levels and plays a significant role in fat storage. It helps cells absorb glucose to be used for energy or stored for future use. However, when insulin levels are consistently high, typically due to a diet high in sugars and refined carbohydrates, it can lead to weight gain and even insulin resistance, a condition where the body’s cells become less responsive to insulin.
Insulin resistance is a key factor in obesity and metabolic syndrome, making it a crucial hormone to understand in the context of weight loss. This section will explore how dietary choices and lifestyle habits can improve insulin sensitivity, thus aiding in weight management. It will provide practical recommendations for a balanced diet and lifestyle modifications that can help regulate insulin levels. This insight is particularly beneficial for those struggling with weight loss plateaus or those with a predisposition to metabolic syndrome.
Cortisol and Stress-Related Weight Changes

Cortisol, commonly known as the stress hormone, plays a significant role in various body functions, including metabolism and fat storage. It is produced by the adrenal glands in response to stress and has a direct impact on weight, especially around the midsection. Chronic stress leads to prolonged cortisol secretion, which can cause increased appetite, cravings for unhealthy foods, and a tendency to store abdominal fat. Understanding the relationship between stress, cortisol, and weight gain is crucial for effective weight management.
This section will explore strategies to manage stress and, consequently, cortisol levels. Techniques such as mindfulness, yoga, and regular exercise not only reduce stress but also help in balancing cortisol levels. Moreover, certain dietary adjustments can support adrenal health and mitigate cortisol’s impact on weight. Emphasizing the importance of stress management in weight loss provides a more comprehensive approach to a healthier lifestyle, acknowledging that mental well-being is as important as physical health.
Leptin and Ghrelin: The Hunger Hormones

Leptin and ghrelin, often referred to as the hunger hormones, play pivotal roles in appetite regulation. Leptin, produced by fat cells, signals the brain to reduce appetite when fat stores are sufficient, while ghrelin, produced in the stomach, stimulates hunger. An imbalance in these hormones can lead to increased hunger and cravings, making it challenging to maintain a healthy weight. This hormonal imbalance is a common obstacle in weight loss journeys, often overlooked in traditional diet and exercise plans.
Addressing the balance of leptin and ghrelin is crucial for successful weight management. This section will discuss how factors like sleep deprivation, high-fat diets, and stress can disrupt these hormones. It will also provide practical tips to naturally regulate these hormones through dietary choices, sleep hygiene, and lifestyle modifications. By focusing on leptin and ghrelin, individuals can gain better control over their appetite and cravings, facilitating a more effective and sustainable weight loss process.
Sex Hormones: Estrogen and Testosterone
Estrogen and testosterone, the primary female and male sex hormones, respectively, also have significant roles in weight management. Estrogen helps regulate metabolism and body weight, and its fluctuation during different life stages, such as menopause, can lead to weight gain. Testosterone, on the other hand, is crucial for building muscle mass and maintaining a healthy fat distribution. Decreases in testosterone levels, a common occurrence in aging men, can lead to decreased muscle mass and increased body fat.
This section will delve into how hormonal changes during life stages like menopause in women and andropause in men can affect body weight. It will provide insights into how to manage weight effectively during these times, including diet, exercise, and potentially hormone replacement therapy under medical guidance. Understanding the impact of sex hormones on weight can help in customizing weight loss strategies that are more effective and tailored to individual hormonal profiles.
The Impact of Sleep on Hormonal Balance

Sleep plays a critical yet often underestimated role in hormonal balance and, by extension, weight management. Adequate sleep is essential for the regulation of numerous hormones, including those directly involved in appetite and metabolism, such as leptin, ghrelin, and insulin. Lack of sleep can disrupt these hormones, leading to increased appetite, cravings for high-calorie foods, and decreased insulin sensitivity, all of which can contribute to weight gain. This section will highlight the connection between sleep quality and hormonal health, emphasizing sleep’s role as a foundational element in weight management.
This section will also offer practical advice for improving sleep quality. It will cover strategies such as establishing a regular sleep schedule, creating a sleep-conducive environment, and limiting exposure to blue light before bedtime. Additionally, the impact of lifestyle choices, such as caffeine and alcohol consumption, on sleep quality will be discussed. By improving sleep, individuals can better regulate the hormones that influence their weight, thus making their weight-loss journey more effective.
Practical Steps for Balancing Hormones

Balancing hormones is a multifaceted approach that involves diet, exercise, lifestyle changes, and possibly medical interventions. This final section will summarize practical steps that individuals can take to balance their hormones for effective weight loss. It will reiterate the importance of a balanced diet rich in whole foods, regular physical activity, and stress management techniques. Furthermore, it will emphasize the need to address any underlying medical conditions that may be impacting hormonal balance.
The section will also stress the importance of a personalized approach, acknowledging that hormonal imbalances vary from person to person. It will encourage readers to consult healthcare professionals for personalized advice, especially in cases of suspected hormonal disorders. By implementing these practical steps, individuals can work towards balancing their hormones, thereby facilitating a more effective and sustainable weight loss journey. This holistic approach to weight management acknowledges the complexity of the human body and the multitude of factors that influence weight.
Harmonizing Hormones for Weight Loss Success
From the metabolism-regulating thyroid hormones to the appetite-controlling leptin and ghrelin and the stress-associated cortisol, it’s clear that hormonal balance is key to successful weight management. Understanding and managing these hormonal influences can lead to more effective and sustainable weight loss strategies. As we wrap up, remember that a holistic approach, encompassing diet, exercise, stress management, and adequate sleep, is crucial for harmonizing hormones and achieving lasting weight loss success.