When discussing weight loss, the significance of diet cannot be overstated, and among the myriad of nutrients essential for managing weight, dietary fiber stands out for its unique benefits. This post highlights the pivotal role of fiber in weight loss, exploring its impact on digestion, calorie intake, gut health, and overall dietary satisfaction. By understanding how fiber contributes to weight management, individuals can make informed choices that support their health and weight loss goals. Through an in-depth examination of dietary fiber, from its basic definitions to practical advice on intake, this post aims to empower you with the knowledge you need to leverage fiber for effective weight loss.
The Basics of Dietary Fiber

Dietary fiber, often heralded as a cornerstone of healthy eating, is a plant-based nutrient that the body cannot digest or absorb. Unlike other food components such as fats, proteins, or carbohydrates, which the body breaks down and absorbs, fiber passes relatively intact through the digestive system. There are two main types of dietary fiber: soluble and insoluble. Soluble fiber dissolves in water to form a gel-like material, which can help lower blood cholesterol and glucose levels. Insoluble fiber, on the other hand, promotes the movement of material through the digestive system and increases stool bulk, aiding in constipation relief.
Each type of fiber plays a distinct role in maintaining health, yet they both contribute to weight management and loss. Soluble fiber’s ability to form a viscous gel slows down the process of digestion, leading to a prolonged feeling of fullness. Insoluble fiber, while not digestible, adds bulk to the diet, helping individuals feel satisfied with fewer calories. Together, these fibers work synergistically to prevent overeating by extending the duration of satiety after meals. Understanding these basic mechanisms highlights the importance of incorporating a variety of fiber-rich foods into the diet for effective weight management.
Fiber’s Role in Digestion
The digestion-slowing effect of fiber is a key factor in its ability to aid weight loss. By moderating the rate at which nutrients are absorbed, fiber helps maintain a steady blood sugar level, reducing the likelihood of insulin spikes and subsequent hunger pangs. This regulation of digestion encourages a more controlled appetite and can significantly curb unnecessary snacking or overeating. Soluble fiber, in particular, has a profound impact on this process, as its gel-forming properties delay the emptying of the stomach and the absorption of glucose.
Moreover, this delayed digestion process means that the feeling of fullness lasts longer, effectively reducing overall calorie intake without the need for restrictive dieting. The presence of fiber in the stomach signals to the brain that enough food has been consumed, thereby decreasing the desire to eat more. This natural appetite control is a fundamental aspect of why fiber is so effective for weight loss. By integrating more high-fiber foods into meals, individuals can enjoy longer periods of satisfaction and naturally reduce their calorie consumption.
Fiber and Calorie Intake

Incorporating fiber into the diet is a strategy that impacts calorie intake directly and indirectly. Foods high in dietary fiber, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes, are often lower in calories compared to their low-fiber counterparts. This means that by choosing fiber-rich foods, individuals can eat larger volumes of food while consuming fewer calories, a concept central to feeling satisfied on a weight loss diet without feeling deprived. The bulk provided by fiber-rich foods also contributes to a sense of fullness, further aiding in the reduction of overall calorie intake.
Additionally, the energy required to chew and digest high-fiber foods can slightly increase the body’s energy expenditure, contributing to weight loss. Although the effect is modest, it illustrates the comprehensive role fiber plays in managing body weight. By selecting high-fiber options, individuals not only reduce their calorie intake but also engage their digestive systems in a way that can help burn more calories. This dual action reinforces the importance of dietary fiber as a tool for weight management and underscores the benefits of making high-fiber choices a staple in any weight-loss diet.
Fiber’s Impact on Gut Health

The benefits of fiber extend beyond simple digestion and calorie control; it also plays a crucial role in maintaining a healthy gut microbiome. The soluble fiber found in foods acts as a prebiotic, providing nourishment for beneficial gut bacteria. This relationship between fiber and gut flora is significant because a diverse and healthy microbiome is linked to improved digestion, enhanced immune function, and even a lower risk of obesity. By fostering a healthy gut environment, fiber contributes to more than just weight management; it supports overall health and well-being.
Emerging research suggests that a healthy gut microbiome can influence weight loss directly by affecting metabolism and indirectly by improving mood, which can reduce emotional eating. Additionally, certain types of gut bacteria are known to influence how the body metabolizes fiber, producing short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) that have been linked to reduced inflammation and improved gut health. These SCFAs can also help regulate appetite and increase energy expenditure. Thus, by supporting a healthy gut microbiome, dietary fiber plays a multifaceted role in weight loss and overall health, making it an indispensable component of a balanced diet.
How Much Fiber Do You Need?
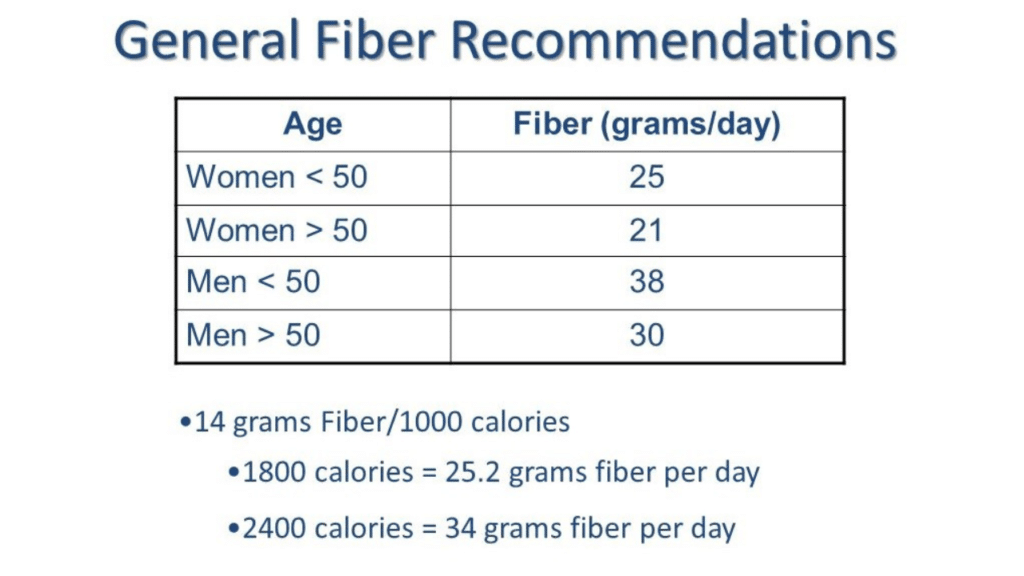
Understanding the daily fiber intake recommendations is crucial for harnessing fiber’s full benefits for weight loss and health. Health experts suggest that women aim for about 25 grams of fiber per day, while men should target around 38 grams. However, the average person’s diet falls significantly short of these numbers, often leading to missed opportunities for health improvement and weight management. Meeting these fiber intake goals can support digestion, maintain satiety, and reduce the risk of chronic diseases such as diabetes and heart disease.
Increasing fiber intake to meet these recommendations can be achieved through dietary adjustments that emphasize whole foods. It’s important to increase fiber gradually to allow the body to adjust, minimizing potential discomfort such as bloating or gas. Equally, ensuring adequate water intake alongside higher fiber consumption is essential, as fiber absorbs water to help move smoothly through the digestive system. By making incremental changes to include more fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes in meals, individuals can easily meet or even surpass the recommended daily fiber intake, reaping the numerous health benefits fiber offers.
Sources of High-Fiber Foods
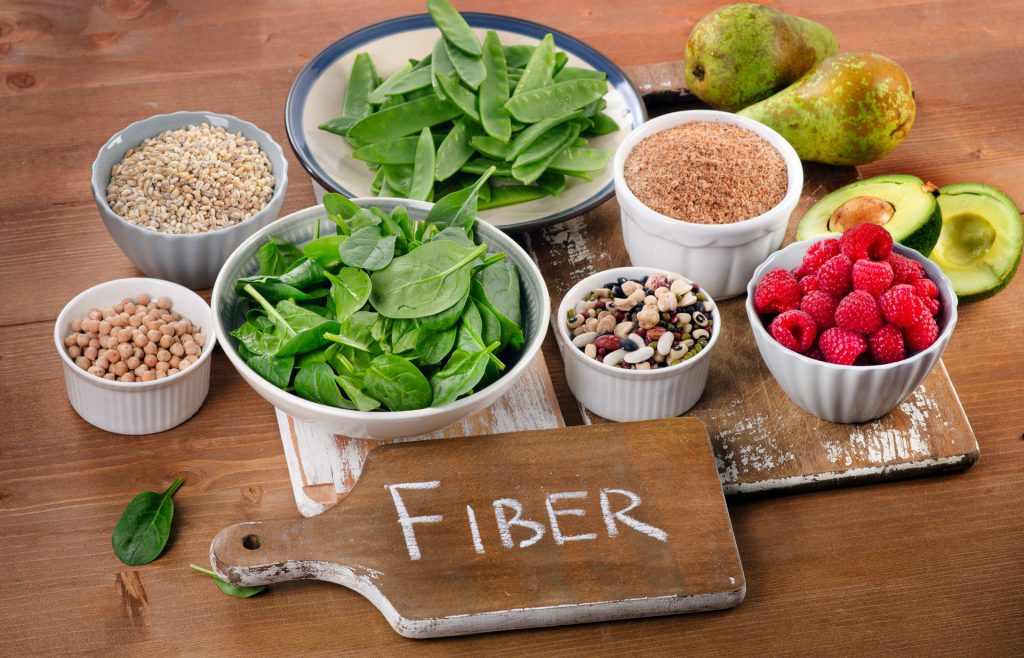

Identifying and incorporating high-fiber foods into one’s diet is a straightforward strategy for enhancing weight loss efforts and improving overall health. Foods rich in fiber include fruits (such as raspberries, apples, and pears), vegetables (like green peas, broccoli, and Brussels sprouts), legumes (including lentils, black beans, and chickpeas), whole grains (such as barley, quinoa, and oats), nuts, and seeds. These foods provide the much-needed dietary fiber and come packed with a host of other nutrients beneficial for health, making them an excellent choice for anyone looking to improve their diet.
Incorporating these high-fiber foods into meals and snacks doesn’t have to be challenging. Simple swaps like choosing whole grain bread over white, adding beans to salads, or opting for fruit as a snack instead of processed foods can significantly increase fiber intake. Additionally, experimenting with diverse cuisines and recipes can make adding fiber to the diet both enjoyable and delicious. By focusing on whole and minimally processed foods, individuals can easily increase their fiber intake, contributing to weight loss and promoting a healthier digestive system.
Fiber Supplements vs. Natural Sources

While getting fiber from food is the ideal way to meet daily requirements, there are circumstances where fiber supplements might be beneficial. Supplements can help individuals who struggle to consume enough fiber through diet alone due to dietary restrictions, food allergies, or specific health conditions. However, it’s essential to recognize that fiber supplements don’t offer the same broad spectrum of nutrients that whole foods provide. Therefore, they should complement, not replace, a diet rich in natural sources of fiber.
Before adding a fiber supplement to your regimen, consulting with a healthcare provider is advisable to ensure it’s appropriate for your specific health needs and won’t interact with any medications. When choosing a supplement, opting for those that are well-researched and free from unnecessary additives is crucial. Despite their convenience, supplements should be viewed as a temporary aid rather than a long-term solution. Prioritizing natural sources of fiber ensures the intake of a wide range of beneficial nutrients alongside fiber, supporting overall health beyond just weight management.
Make Fiber Your Weight Loss Friend
Embracing fiber’s role in weight management unlocks a pathway to a healthier, more balanced lifestyle. By integrating a variety of fiber-rich foods into your diet, you not only aid in weight loss but also support your overall health, from digestion to disease prevention. Start today by making simple swaps and choices that increase your fiber intake, ensuring a fuller, more satisfying journey toward your weight management goals. Let fiber be your ally in achieving the healthy body you deserve.